Indianapolis, Indiana – Defendant Circle City Broadcasting, LLC d/b/a WISH-TV, is being sued by Plaintiff Christopher Sadowski over alleged copyright infringement. Sadowski is a photojournalist from New Jersey, who has been published in numerous popular newspapers and magazines. While he holds the licenses to his photographs, court documents explain that Sadowski allows entities to purchase a one-time-use license for themselves.
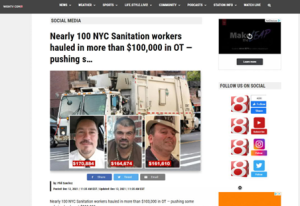 According to the complaint, in 2019, Sadowski created and copyrighted a photograph titled “062219garbagetruck4CS,” depicting the bustling streets of New York City. In 2021, Circle City Broadcasting purportedly published Sadowski’s work on their website, without obtaining the necessary licensing. It is alleged that not only did they display the image without consent, but they also cropped out Sadowski’s copyright management information, potentially infringing upon his rights.
According to the complaint, in 2019, Sadowski created and copyrighted a photograph titled “062219garbagetruck4CS,” depicting the bustling streets of New York City. In 2021, Circle City Broadcasting purportedly published Sadowski’s work on their website, without obtaining the necessary licensing. It is alleged that not only did they display the image without consent, but they also cropped out Sadowski’s copyright management information, potentially infringing upon his rights.
Despite Sadowski’s supposed attempts to resolve the matter amicably, Circle City Broadcasting purportedly failed to address the issue satisfactorily. Consequently, Sadowski pursued legal action to address the alleged willful infringement.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News