Indianapolis, Indiana – District Judge Tanya Walton Pratt of the Southern District of Indiana denied Plaintiff’s request for partial summary judgment for declaratory relief and injunctive relief against Defendants in a copyright dispute over the use of Plaintiff’s copyrighted photograph of Indianapolis.
This lawsuit dates back to June 7, 2011 when Plaintiff Richard N. Bell of McCordsville, Indiana sued 22 Defendants for alleged infringement of his copyrighted photo, U.S. Copyright Registration No. VA0001785115. Bell amended his complaint multiple times, with the third amended complaint becoming the operative pleading on December 6, 2012.
In May 2013, the litigation was severed into three separate cases, including the one that is the subject of this opinion. In this lawsuit, Bell, who is both an Indiana copyright attorney and a professional photographer, accused Defendants Insurance Concepts, Fred O’Brien and Shanna Cheatham of copyright infringement. Bell sought injunctive relief along with damages, costs and attorney’s fees.
A prior opinion by the court held for these Defendants on the issues of Bell’s state law claims and copyright damages claims. In this order, the court addressed the parties’ cross motions for partial summary judgment on the remaining issues – declaratory and injunctive relief.
The court first cited the four-factor test necessary to obtain an injunction, which states that a plaintiff must show:
(1) that it has suffered an irreparable injury; (2) that remedies available at law, such as monetary damages, are inadequate to compensate for that injury; (3) that, considering the balance of hardships between the plaintiff and defendant, a remedy in equity is warranted; and (4) that the public interest would not be disserved by a permanent injunction.
The court noted that in a prior ruling, it had concluded that Bell had failed to establish any damages, including no damages that would rise to the level of “irreparable injury.” Consequently, the first factor was not met. The court then opined that an injunction was also unwarranted under the second factor, as Bell could again institute litigation upon finding any future copyright violations by a Defendant. Having found that at least two of the four elements required for an injunction were missing, the court declined to address the remaining factors.
The court similarly declined to exercise its discretion to grant declaratory relief on the grounds that, after having been notified, the Defendants had promptly removed the copyrighted photo and, moreover, the websites on which the photo had been published no longer existed. As such, it concluded that there was no “substantial controversy, between parties having adverse legal interests, of sufficient immediacy and reality to warrant the issuance of a declaratory judgment.”
The court consequently denied Plaintiff Bell’s motion for partial summary judgment and his request for declaratory and injunctive relief. Defendants’ motion for partial summary judgment was granted.
Practice Tip:
• Attorney/Photographer Sues Georgia Real Estate Company for Infringing Copyrighted Photo
• Sovereign Immunity May Take a Toll on Bell’s Latest Copyright Lawsuit
• Appellate Court Dismisses Copyright Appeal as Premature
• Bell Rings in the Holiday Weekend with a New Copyright Lawsuit
• Bell Files New Copyright Infringement Lawsuit
• Bell Sues Georgia-Base FindTicketsFast.com for Copyright Infringement
• Richard Bell Files Two New Copyright Infringement Lawsuits
• Court Prevents Copyright Plaintiff Bell from Outmaneuvering Legal System; Orders Bell to Pay Almost $34,000 in Fees and Costs
• Three Default Judgments of $2,500 Ordered for Copyright Infringement• Court Orders Severance of Misjoined Copyright Infringement Complaint
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News









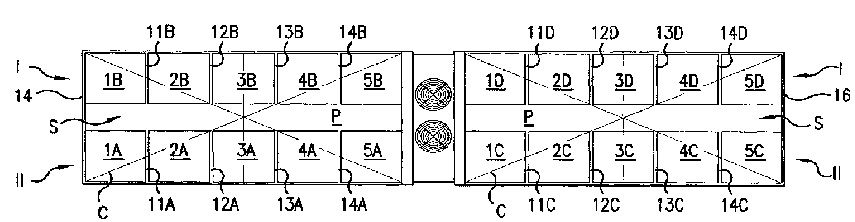 Vincent P. Tippmann Sr. Family, LLC (“Tippmann Family, LLC”) claims ownership of the patent-in-suit, a technology that facilitates rapid and efficient freezing and thawing of food products. It also indicates that it is the inventing and owning company of various patents and patent applications related to apparatuses and methods for blast freezing and/or thawing of products.
Vincent P. Tippmann Sr. Family, LLC (“Tippmann Family, LLC”) claims ownership of the patent-in-suit, a technology that facilitates rapid and efficient freezing and thawing of food products. It also indicates that it is the inventing and owning company of various patents and patent applications related to apparatuses and methods for blast freezing and/or thawing of products.