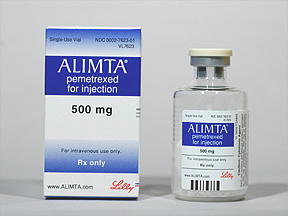
Indianapolis, Indiana – In conjunction with co-counsel, an Indiana patent attorney for Eli Lilly and Company of Indianapolis, Indiana sued in the Southern District of Indiana alleging infringement by Sandoz Inc. of Princeton, New Jersey of ALIMTA®, Patent No. 7,772,209, which was issued by the U.S. Patent Office.
ALIMTA, which is licensed to Lilly, is a chemotherapy agent used for the treatment of various types of cancer. ALIMTA is composed of the pharmaceutical chemical pemetrexed disodium. It is indicated, in combination with cisplatin, (a) for the treatment of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma, or (b) for the initial treatment of locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. ALIMTA also is indicated as a single agent for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer after prior chemotherapy. Additionally, ALIMTA is indicated for maintenance treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer whose disease has not progressed after four cycles of platinum-based first-line chemotherapy. One or more claims of the ‘209 patent cover a method of administering pemetrexed disodium to a patient in need thereof that also involves administration of folic acid and vitamin B12.
This Indiana patent infringement lawsuit arises out of the filing by Defendant of an Abbreviated New Drug Application (“ANDA”) with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) seeking approval to manufacture and sell generic versions of ALIMTA prior to the expiration of the ‘209 patent. Defendant filed as a part of that ANDA a certification of the type described in Section 505(j)(2)(A)(vii)(IV) of the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, 21 U.S.C. § 55(j)(2)(A)(vii)(IV), with respect to the patent-in-suit, asserting that the claims of the patent-in-suit are invalid, unenforceable, and/or not infringed by the manufacture, use, offer for sale, or sale of Defendant’s ANDA products.
In its complaint, filed by an Indiana patent lawyer, Lilly states that Defendant intends to engage in the manufacture, use, offer for sale, sale, marketing, distribution, and/or importation of Defendant’s ANDA products and the proposed labeling therefor immediately and imminently upon approval of the ANDA i.e., prior to the expiration of the patent-in-suit. Lilly asserts that Defendant’s actions constitute and/or will constitute infringement of the patent-in-suit, active inducement of infringement of the patent-in-suit, and contribution to the infringement by others of the patent-in-suit.
The complaint lists a single claim: Infringement of U.S. Patent No. 7,772,209. Lilly asks the court for the following relief:
(a) A judgment that Sandoz has infringed the ‘209 patent and/or will infringe, actively induce infringement of, and/or contribute to infringement by others of the ‘209 patent;
(b) A judgment ordering that the effective date of any FDA approval for Sandoz to make, use, offer for sale, sell, market, distribute, or import Sandoz’s ANDA Products, or any product the use of which infringes the ‘209 patent, be not earlier than the expiration date of the ‘209 patent, inclusive of any extension(s) and additional period(s) of exclusivity;
(c) A preliminary and permanent injunction enjoining Sandoz, and all persons acting in concert with Sandoz, from making, using, selling, offering for sale, marketing, distributing, or importing Sandoz’s ANDA Products, or any product the use of which infringes the ‘209 patent, or the inducement of or contribution to any of the foregoing, prior to the expiration date of the ‘209 patent, inclusive of any extension(s) and additional period(s) of exclusivity;
(d) A judgment declaring that making, using, selling, offering for sale, marketing, distributing, or importing of Sandoz’s ANDA Products, or any product the use of which infringes the ‘209 patent, prior to the expiration date of the ‘209 patent, infringes, will infringe, will actively induce infringement of, and/or will contribute to the infringement by other of the ‘209 patent;
(e) A declaration that this is an exceptional case and an award of attorneys’ fees pursuant to 35 U.S.C. § 285; and
(f) An award of Lilly’s costs and expenses in this action.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News




 Yamaguchi, Japan sued in the
Yamaguchi, Japan sued in the  Hünenberg, Switzerland sued in the
Hünenberg, Switzerland sued in the  Jersey; and
Jersey; and  filed a lawsuit in the
filed a lawsuit in the  Illinois (also known as “John Deere”) infringed the patented “Combine Header Height Control“,
Illinois (also known as “John Deere”) infringed the patented “Combine Header Height Control“,