Fort Wayne, Indiana – An Indiana intellectual property attorney for Global Archery Products, Inc. of Ashley, Indiana commenced litigation in the Northern District of Indiana alleging trademark and patent infringement by Jordan Gwyther d/b/a Larping.org and UpshotArrows.com of Seattle, Washington.
Two patents are at issue in this lawsuit: U.S. Patent No. 8,449,413 (the “`413 Patent”) and U.S. Patent No. 8,932,159 (the “`159 Patent”). Both are entitled “Non-Lethal Arrow.” Also at issue are U.S. Trademark Registration No. 4,208,867 and 4,208,868 for ARCHERY TAG for use in connection with non-lethal arrows. The patents and trademarks have been registered by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
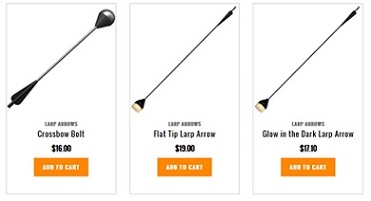
Global contends that Jordan Gwyther d/b/a Larping.org (“Larping”) is selling and offering for sale several products including a “Crossbow Bolt,” a “Flat Tip Larp Arrow,” a “Glow in the Dark Larp Arrow” and a “Round Tip Larp Arrow.” These arrows are marketed at www.upshotarrows.com. Global asserts that Larping is violating Global’s trademark rights by, inter alia, using the ARCHERY TAG trademark on advertising and as a paid “key word” on one or more search engines in connection with the marketing of these products. Global also claims that Larping’s products infringe upon two of Global’s patents.
In addition to patent infringement and trademark infringement, Global asserts various additional claims against Larping. The counts listed in this federal lawsuit are as follows:
• Count I: Infringement of the ‘413 Patent by Larping
• Count II: Infringement of the ‘159 Patent by Larping
• Count III: Infringement of Federal Trademarks
• Count IV: False Designation of Origin/Unfair Competition
• Count V: False Advertising
• Count VI: Tortious Interference with Contractual Relations
• Count VII: Tortious Interference with Business Relationships
• Count VIII: Criminal Mischief• Count IX: Deception
Global seeks equitable relief along with damages, including punitive damages, costs and attorney fees.