Indianapolis, Indiana – Magistrate Judge Denise K. LaRue, writing for the Southern District of Indiana, directed the Clerk of the Court to sever all but one defendant from the copyright infringement complaint of Richard Bell, an Indiana copyright attorney. Bell was also ordered by the court to pay separate filing fees for each new cause of action.
Bell is a copyright lawyer and a professional photographer. He contends that he is the owner of two copyrighted photographs of Indianapolis taken in March 2000. The photos have been registered with the U.S. Copyright Office.
In April, Bell filed another copyright infringement lawsuit in the Southern District of Indiana alleging copyright infringement of his photos by numerous Defendants. The Defendants were: Diversified Vehicle Services of Marion County, Indiana; Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rhonda Williams of Indianapolis, Indiana; Forensic Solutions, Inc. of Waterford, New York; Heath Garrett of Nashville, Tennessee; CREstacom, Inc. of Fishers, Indiana; American Traveler Service Corp LLC, location unknown; Mike Cowper of Martinsville, Indiana; Kimberly Hinds of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute of Troy, New York; EasyStreet Realty of Indianapolis, Indiana; Drohan Management of Reston, Virginia; Metal Markets of Indianapolis, Indiana; Mattison Corporation of Indianapolis, Indiana; Industrial Heating Equipment Association of Taylor Mill, Kentucky; Junk Dawgs of Indianapolis, Indiana and WRTV of Indianapolis, Indiana. Bell is both the copyright lawyer and Plaintiff in this lawsuit.
In this earlier complaint, Bell alleged that each Defendant, independent of each other Defendant, “created their individual website to promote and market their business” and placed the Plaintiff’s copyrighted photo on each of the Defendants’ respective websites. Claiming copyright infringement, unfair competition and theft, Bell asked the court for, inter alia, the maximum allowable statutory damages for each copyright violation.
The court ordered Bell to show cause why all defendants but one should not be severed for misjoinder. Bell argued that the rules regarding joinder should be given a broad scope so that multiple lawsuits could be avoided.
The court was not persuaded. In addressing Bell’s contention that joinder of the unrelated Defendants was proper, it was Bell’s own language, and the factual underpinnings of that language, to which the court pointed in denying joinder. The court noted that Bell’s “complaint alleges that ‘[e]ach defendant, independently of each other, created or had created a website to promote and advertise the business of each Defendant,’ and that Plaintiff discovered that ‘the website [of] each of these Defendants contained [one of the photographs].'” The court also noted that “[e]xcept for defendants Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions, the Complaint contains no allegation that any defendant acted in concert with another defendant in appropriating Plaintiff’s photographs and it does not allege any transaction, occurrence, or series of transactions or occurrences in which two or more defendants participated.” (Citations omitted.)
The court then reviewed the requirements of Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 20(a)(2)(A) that a Plaintiff’s claims against defendants joined in the same action must respect or arise out of the same occurrence or the same series of occurrences. While Bell had alleged copyright infringement of the same copyrighted material against all Defendants, the court held this to be insufficient. Similarly, while the same types of questions of fact would arise against each Defendant – “e.g., how did the defendant find Plaintiff’s photograph, what did the defendant know about the photograph’s copyright status, did the defendant make commercial use of the photograph, and did the defendant pay for the use of the photograph” – those similar questions of fact provided no logical relationship among the Defendants that would support joinder.
Instead, the court found that each Defendant was accused of independently committing separate and distinct acts of copyright infringement that happened to involve the same photograph.
The court then directed the Clerk of the Court to sever all defendants other than Diversified Vehicle Services from the complaint as it had been filed and to open separate causes for each of the severed defendants, with the exception of defendants Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions, which the court directed to be joined in one cause. WRTV was dropped, as Bell indicated that it had been included as a defendant inadvertently.
The court also ordered Bell to pay the $400 filing fee for each of the 15 severed causes of action no later than June 2, 2014.
Practice Tip #1: There has been a growing trend of attempting to monetize copyright infringement. In this particular case, the docket for the initial complaint showed Bell’s demand to be $5,000,000 for the alleged infringing activities. In ruling that “unrelated claims against unrelated defendants belong in different suits, in part to ensure that plaintiffs pay the required filing fees” and subsequently ordering the Plaintiff to pay a separate filing fee for each of the Defendants, Magistrate Judge LaRue has employed one approach that may be useful in combatting such copyright trolling.
Practice Tip #2: Under 17 U.S.C. § 504(c)(1), a copyright owner may elect actual or statutory damages. Statutory damages range from a sum of not less than $750 to not more than $30,000 per infringed work.
Practice Tip #3: The claims of this case appear calculated to trigger the “advertising injury” clause of many general business liability insurance policies. If a defendant has applicable business insurance, this may allow Bell to negotiate quicker settlements. Overhauser Law Offices, publisher of this Site, counsels clients on insurance coverage for insurance claims.
Practice Tip #4: These latest causes of actions represent the most recent of three ongoing cases filed by Bell asserting infringement of his photos. We have blogged about his copyright infringement litigation before. See here. The Indiana Lawyer also wrote recently about Bell’s copyright litigation. That article includes an interview with Paul B. Overhauser, Managing Partner of Overhauser Law Offices.
Continue reading

 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News


 Indianapolis, Indiana – In 2013, a federal indictment including counts of theft of trade secrets belonging to
Indianapolis, Indiana – In 2013, a federal indictment including counts of theft of trade secrets belonging to  the
the 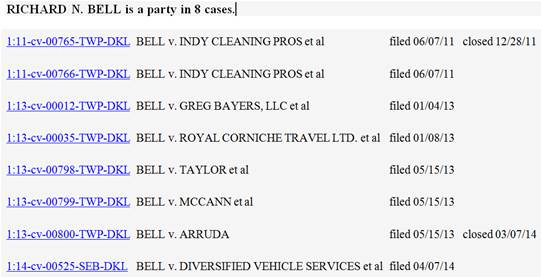 Defendants are: Diversified Vehicle Services of Marion County, Indiana; Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rhonda Williams of Indianapolis, Indiana; Forensic Solutions, Inc. of Waterford, New York; Heath Garrett of Nashville, Tennessee; CREstacom, Inc. of Fishers, Indiana; American Traveler Service Corp LLC, location unknown;
Defendants are: Diversified Vehicle Services of Marion County, Indiana; Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rhonda Williams of Indianapolis, Indiana; Forensic Solutions, Inc. of Waterford, New York; Heath Garrett of Nashville, Tennessee; CREstacom, Inc. of Fishers, Indiana; American Traveler Service Corp LLC, location unknown; “STRATOTONE” (the “Stratotone mark”),
“STRATOTONE” (the “Stratotone mark”),  attorneys for
attorneys for 