In 2008, a new federal law creating stricter penalties for criminals who engaged in intellectual property theft was enacted to keep pace with globalization, e-commerce, and technology advances.
Fast forward to 2016: Technological advances continue at an even faster pace, dramatically
|
|
Intellectual Property Theft 101
Intellectual property can be an idea, an invention, a design, a business process, or even a creative expression. All are protectable under the law.
Once stolen, intellectual property can generate a great deal of money for the thieves. But there are other consequences. Intellectual property theft, which includes theft of trade secrets, the trafficking of counterfeit goods, and digital piracy, results in billions of dollars in lost profits annually. Failure to protect the nation’s intellectual property undermines confidence in the economy, removes opportunities for growth, erodes America’s technological advantage, and disrupts fairness and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Some intellectual property thefts pose a more far-reaching and serious threat to the U.S. than economic loss to the rights holders. These thefts can also put public safety at risk through the sale of counterfeit pharmaceuticals,
electrical components, and aircraft and automobile parts, as well as through the funding of other kinds of crime.
Within its intellectual property rights violations program, the FBI prioritizes its investigations and focuses the majority of its resources on cases involving theft of trade secrets, counterfeit goods that pose a threat to human health and safety, and copyright and infringement matters with a nexus to national security or organized crime or that pose a significant economic impact.
Along with its partners at the National Intellectual Property Rights Coordination Center, the FBI also participates in several intelligence-driven national initiatives, including:
–
Operation Chain Reaction, which focuses on counterfeit products entering the U.S. government supply chain that pose a threat to human health and safety or national security;
–
Operation Engine Newity, which addresses counterfeit automotive parts that threaten safety, including airbags, brake pads, and steering systems; and
–
Operation Apothecary, which focuses on counterfeit pharmaceuticals that pose a safety threat.
|
|
increasing the threat posed by criminals who steal trade secrets, produce and/or traffic in counterfeit products, and infringe on copyrights. One important factor in this increase is the global expansion of online marketplaces, which aids international and domestic criminal organizations in trafficking in counterfeit goods.
The Department of Justice recently announced a new strategy that involves partnering more closely with businesses in an effort to combat these types of crimes more effectively. According to Attorney General Loretta Lynch, “Through this new approach, we intend to provide information and resources to individuals and companies that will help them identify and disrupt attempts on their intellectual property, extend greater protection to American commerce as a whole, and safeguard the health and safety of individual Americans.” The Federal Bureau of Investigations (“FBI”), working with its investigative partners at the National Intellectual Property Rights Coordination Center (“NIPRCC”), will play an integral part in this strategy.
The FBI has already been collaborating for years with brand owners, copyright holders, and trademark holders because in an effort to prevent the harm that intellectual property theft causes: legitimate businesses lose billions of dollars in revenue and suffer damaged reputations, consumer prices go up, the U.S. and global economies are robbed of jobs and tax revenue, product safety is reduced, and sometimes lives are even put at risk. The FBI’s efforts with these businesses to date have involved shared information, aggressive criminal initiatives based on current or emerging trends, and investigations.
The FBI has now begun expanding its efforts to work with third-party entities, such as online marketplaces, payment service providers, and advertisers, that may inadvertently enable the activities of criminals.
Third-party online marketplaces draw consumers to their sites with competitive pricing and a sense of security, but criminal counterfeiters exploit these marketplaces to gain an appearance of legitimacy, access to far-reaching advertising, and efficient sales transactions.
Payment service providers, such as credit card payment processors and related payment alternatives, also give counterfeiters the appearance of legitimacy when they provide payment options that consumers mistakenly interpret to mean that the businesses they service are legitimate.
Online advertising systems and platforms enable website owners to outsource the process of monetizing their website traffic. Criminals have begun exploiting advertising as an alternative revenue stream, drawing traffic to their sites by offering counterfeit products for sale or pirated digital content for download.
The FBI finds that there are significant benefits to working with these third-party entities. According to David Farquhar, who heads up the FBI’s Intellectual Property and Cyber-Enabled Crimes Unit at the NIPRCC, “We’re not only broadening awareness of the crime problem, we can also obtain information about crime trends, get investigative leads that will help us identify criminals, and collect evidence of criminal activity.” Farquhar added that the FBI will assist these companies with refining their own analytical tools and techniques for uncovering fraud.
Also new in its approach to intellectual property theft is an enhanced relationship between the FBI’s criminal and counterintelligence personnel when working theft of trade secrets cases. A trade secrets case worked under the counterintelligence program, which occurs when the involvement of state-sponsored actors is suspected, will be referred to a criminal squad if no state sponsorship is found. And when criminal investigators begin to suspect the involvement of a state sponsor, the case will be referred to the counterintelligence squad.
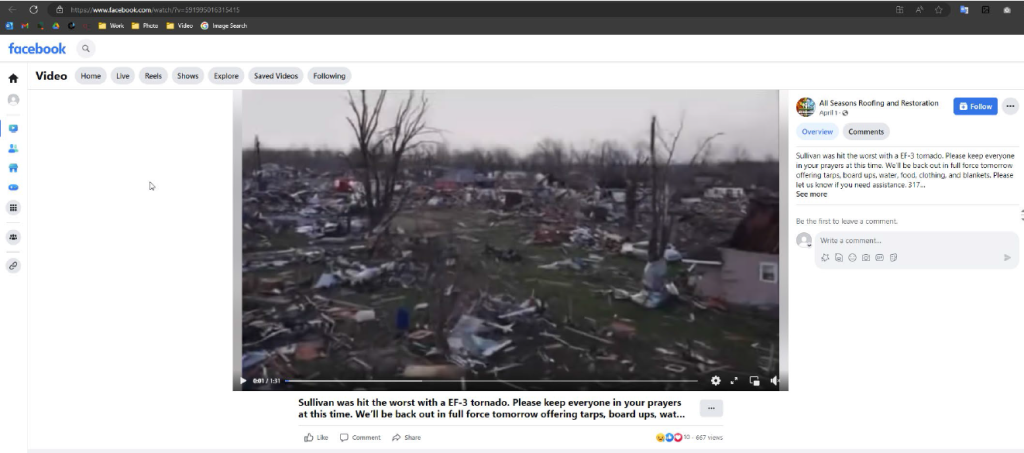 According to the complaint, Aaron Rigsby recorded and produced a video capturing the aftermath of a tornado in Sullivan, Indiana. Rigsby then secured copyright registrations for his work, establishing his exclusive rights to its use and distribution.
According to the complaint, Aaron Rigsby recorded and produced a video capturing the aftermath of a tornado in Sullivan, Indiana. Rigsby then secured copyright registrations for his work, establishing his exclusive rights to its use and distribution. Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News






![hdl-test-strips2-new[1].jpg](https://www.iniplaw.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/366/2016/10/hdl-test-strips2-new1.jpg)